Understanding Measures
In everyday life and in many jobs, we need to measure different quantities. The main types of measures we'll cover here are length, weight (mass), and capacity (volume of liquids).
It's important to be familiar with common units for each type of measurement and how to convert between them.
Length
Length measures how long something is, or the distance between two points. Common units include millimetres (mm), centimetres (cm), metres (m), kilometres (km), and miles.
Common Length Conversions:
Visualizing Metric Length Conversions
The diagram below helps visualize the relationships between common metric units of length: millimetres (mm), centimetres (cm), metres (m), and kilometres (km).
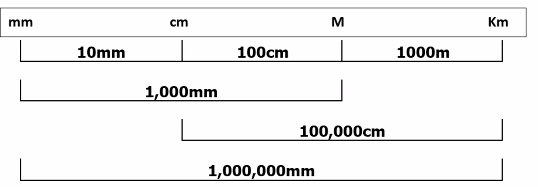
Key takeaways from the diagram:
- To go from a smaller unit to a larger unit (e.g., mm to cm, cm to m, m to km), you generally divide by 10, 100, or 1000 respectively.
- To go from a larger unit to a smaller unit (e.g., km to m, m to cm, cm to mm), you multiply by 1000, 100, or 10 respectively.
- The diagram also illustrates larger jumps:
1 metre = 1000 millimetres(1m = 100cm, and 1cm = 10mm, so 100 x 10 = 1000)1 kilometre = 100,000 centimetres(1km = 1000m, and 1m = 100cm, so 1000 x 100 = 100,000)1 kilometre = 1,000,000 millimetres(1km = 1000m, 1m = 1000mm, so 1000 x 1000 = 1,000,000)
Understanding these relationships is crucial for converting between units accurately. For example, if you need to convert 2.5 metres to millimetres, you would multiply by 1000 (2.5 m * 1000 = 2500 mm).
| From | To | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Millimetres (mm) | Centimetres (cm) | Divide by 10 (10 mm = 1 cm) |
| Centimetres (cm) | Metres (m) | Divide by 100 (100 cm = 1 m) |
| Metres (m) | Kilometres (km) | Divide by 1000 (1000 m = 1 km) |
| Kilometres (km) | Metres (m) | Multiply by 1000 |
| Metres (m) | Centimetres (cm) | Multiply by 100 |
| Centimetres (cm) | Millimetres (mm) | Multiply by 10 |
| Miles | Kilometres (km) | Multiply by approx. 1.6 (1 mile ≈ 1.6 km) |
| Kilometres (km) | Miles | Divide by approx. 1.6 (or multiply by approx. 0.62) |
Worked Example: Length Conversion
Problem: Convert 3.5 kilometres to metres.
We know 1 km = 1000 m.
So, to convert km to m, we multiply by 1000.
Calculation: 3.5 km × 1000 = 3500 m.
Answer: 3.5 km is 3500 metres.
Weight (Mass)
Weight (more accurately, mass) measures how heavy an object is. Common metric units include grams (g) and kilograms (kg). Imperial units include ounces (oz), pounds (lb), and stones (st).
Common Weight Conversions:
| From | To | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Grams (g) | Kilograms (kg) | Divide by 1000 (1000 g = 1 kg) |
| Kilograms (kg) | Grams (g) | Multiply by 1000 |
| Pounds (lb) | Kilograms (kg) | Multiply by approx. 0.454 (1 lb ≈ 0.454 kg or 1 kg ≈ 2.2 lb) |
| Kilograms (kg) | Pounds (lb) | Multiply by approx. 2.2 |
| Stones (st) | Pounds (lb) | Multiply by 14 (1 stone = 14 lb) |
Worked Example: Weight Conversion
Problem: Convert 2500 grams to kilograms.
We know 1000 g = 1 kg.
So, to convert g to kg, we divide by 1000.
Calculation: 2500 g ÷ 1000 = 2.5 kg.
Answer: 2500 grams is 2.5 kilograms.
Capacity (Volume of Liquids)
Capacity measures how much a container can hold, usually referring to liquids. Common metric units include millilitres (ml), centilitres (cl), and litres (L). Imperial units include pints and gallons.
Common Capacity Conversions:
| From | To | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Millilitres (ml) | Centilitres (cl) | Divide by 10 (10 ml = 1 cl) |
| Centilitres (cl) | Litres (L) | Divide by 100 (100 cl = 1 L) |
| Millilitres (ml) | Litres (L) | Divide by 1000 (1000 ml = 1 L) |
| Litres (L) | Millilitres (ml) | Multiply by 1000 |
| Litres (L) | Centilitres (cl) | Multiply by 100 |
| Centilitres (cl) | Millilitres (ml) | Multiply by 10 |
| Pints | Litres (L) | Multiply by approx. 0.568 (1 pint ≈ 0.568 L) |
| Gallons | Litres (L) | Multiply by approx. 4.546 (1 gallon ≈ 4.546 L) |
| Gallons | Pints | Multiply by 8 (1 gallon = 8 pints) |
Worked Example: Capacity Conversion
Problem: Convert 0.75 litres to millilitres.
We know 1 L = 1000 ml.
So, to convert L to ml, we multiply by 1000.
Calculation: 0.75 L × 1000 = 750 ml.
Answer: 0.75 litres is 750 millilitres.
Exam-Style Measure Problems
1. Ribbon Cutting
A dressmaker has a roll of ribbon that is 5 metres long. She needs to cut pieces that are 25cm long. How many full 25cm pieces can she cut from the roll?
Answer: 20 pieces
Explanation:
- Convert units to be the same. Let's convert metres to centimetres.
5 metres × 100 cm/metre = 500 cm. - Divide the total length by the length of one piece:
500 cm ÷ 25 cm/piece = 20 pieces.
2. Recipe Scaling (Weight)
A recipe for 4 people requires 0.6 kg of flour. How many grams of flour are needed if the recipe is adjusted for 10 people?
Answer: 1500 grams
Explanation:
- Find the amount of flour per person:
0.6 kg ÷ 4 people = 0.15 kg/person. - Calculate flour needed for 10 people:
0.15 kg/person × 10 people = 1.5 kg. - Convert kilograms to grams:
1.5 kg × 1000 g/kg = 1500 g.
3. Filling a Tank (Capacity)
A fish tank holds 75 litres of water. If you use a jug that holds 500 ml, how many full jugs of water will it take to fill the tank?
Answer: 150 jugs
Explanation:
- Convert units to be the same. Let's convert litres to millilitres.
75 litres × 1000 ml/litre = 75000 ml. - Divide the total capacity of the tank by the capacity of one jug:
75000 ml ÷ 500 ml/jug = 150 jugs.
4. Journey Distance (Miles to Kilometres)
A road sign says the next town is 25 miles away. Approximately how far is this in kilometres? (Use 1 mile ≈ 1.6 km).
Answer: Approximately 40 km
Explanation:
- To convert miles to kilometres, multiply by 1.6.
- Calculation:
25 miles × 1.6 km/mile = 40 km.
5. Comparing Weights
Package A weighs 2.3 kg. Package B weighs 2250 g. Which package is heavier and by how many grams?
Answer: Package A is heavier by 50 grams.
Explanation:
- Convert Package A's weight to grams:
2.3 kg × 1000 g/kg = 2300 g. - Compare the weights: Package A is 2300g, Package B is 2250g. So, Package A is heavier.
- Find the difference:
2300 g - 2250 g = 50 g.
Interactive Unit Converter
Converted Value: ?
Key Points for Measures
- Understand the difference between length, weight (mass), and capacity.
- Memorize common conversion factors (e.g., 100cm = 1m, 1000g = 1kg, 1000ml = 1L).
- When converting from a larger unit to a smaller unit, you multiply.
- When converting from a smaller unit to a larger unit, you divide.
- Always check if units are consistent before performing calculations in word problems.